THE BIO-INTELLIGENT SIGNATURE: A LENS ON THE CURRENT AGE
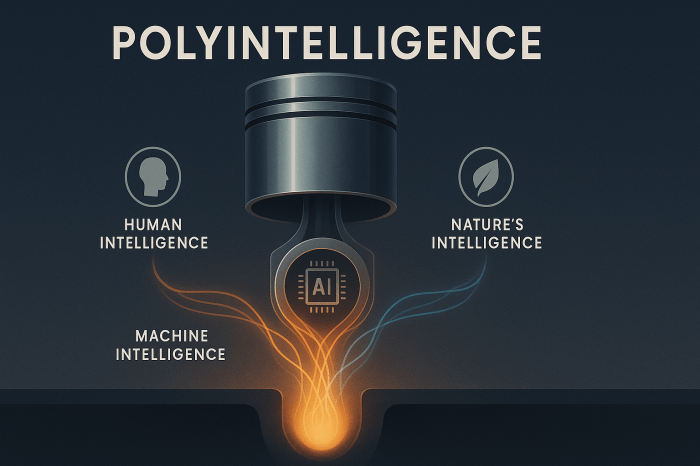
The present moment is shaped by three converging streams of intelligence: machine intelligence, biological intelligence, and planetary intelligence. These are the same sources that form what I have described elsewhere as polyintelligence — cognition distributed across humans, machines, and nature. Each stream is advancing on its own, but their deeper significance appears in how they now influence one another. Artificial intelligence extends cognition beyond the human mind. Synthetic biology brings design and computation into living systems. And the planet — long treated only as a resource base — is increasingly recognized as a source of insight. Through biomimetics, natural systems provide design principles refined through evolution: circularity instead of waste, resilience through diversity, and adaptation through constant sensing and feedback.
Continue reading
