Continue readingThe “free market” is perhaps the most familiar of economic bywords. Since at least the Great Depression, the term has been a staple of the nation’s political discourse, used both to praise and to criticize policy. An economic philosophy intertwined with a number of powerful political ideologies
Jacob Soll – Free Market, The History of an Idea
Economy
A Shift In Economic Power
This visual from visual capitalist looks at global economies between now and 2036. It tracks the shift in economic power across the years, dating back to 2006. This article provides color commentary. The visuals are charts projecting the top ten economies in 2031. The economic domain is one of our convergence areas, with the changing economic landscape contributing to our uncertain environment. In rehearsing the future, this domain is a critical area of focus. What are the implications to the future if the visual accurately depicts economic power shifts?
The Journey: The Building Blocks Of The Future
My previous posts launched a series that will tell the full story of a reimagined future. Described as a journey through the looking glass, the story began with a series description and a look back in time. The series continues, with each post featuring a piece of our journey. We explored the extreme uncertainty of the future in the last post. In this post, I will now dive deeper into the building blocks of the future.
Continue readingThe Economy Is A Critical Area Of Convergence
Much is said about the critical role that science and technology play in shaping the future. This area of convergence continues to have a profound impact on that future. I have described the importance of convergence in various posts in the past, highlighting the impact of other domains like geopolitics, philosophy, and society. Another key domain is the economy. Understanding the global economy is critical to illuminating possible futures. The role of Central Banks has been instrumental in navigating extreme events like COVID-19, as well as the various boom and bust financial cycles of the past.
Continue readingA Possible Future: Automation Shifts The Economic Paradigm
In exploring possible futures, we give ourselves an opportunity to shape them. With all the existing and emerging science and technology building blocks converging with domains like society, the economy, and geopolitics, predicting the future is impossible. But we can look at possibilities and what they mean to our future. One great recent example was described in an article by Tristan Greene. In looking at artificial intelligence and related automation, Mr. Greene focused on how automation could turn capitalism into socialism. This is not a political discussion, rather, it is following a thread to a logical conclusion. In this case, the impact of automation on the future of work. Mr. Greene said:
Continue readingThe Great Demographic Reversal
Beginning in 1990, several forces converged to shape the global economy. Globalization, demographics, technology, deflation, debt, and interest rates have all played a role. Now, according to a recent book, at least two of those forces are reversing. In The Great Demographic Reversal, authors Charles Goodhart and Manoj Pradhan describe these forces and their influence on the last thirty years of economic activity. With this convergence, the world experienced an extended deflationary period, which per the authors, was driven in part by a labor supply shock. The book said the following:
Continue readingReflect, Reimagine, and Reset
“The pandemic represents a rare but narrow window of opportunity to reflect, reimagine, and reset our world.” Klaus Schwab – Founder and Executive Chairman, World Economic Forum
Way back in 2010 when I launched this Blog, its purpose was to focus on reimagining. What will the world look like in twenty years? Ten years into that journey, the word reimagine seems like the right choice. The quote above from Klaus Schwab captures it well. While the pandemic may indeed serve as a catalyst for reflection, reimagining, and an ultimate reset, we have been here before – only to return to the status quo.
Will Coronavirus Accelerate the Path To A Surveillance State?
In a virtual roundtable hosted by C-Level on May 14th, we used several polls to gain insight on how people are thinking about the post-pandemic world. The topic of the roundtable was “Rehearsing Post-Pandemic Futures.” You can view a video of the virtual roundtable Here. I posted the results of polls One, Two and Three earlier. You can participate in those polls by visiting the posts. The fourth poll launched during the session probed the question of surveillance.
Does COVID-19 Accelerate The Loss of Jobs To Automation?
In a virtual roundtable hosted by C-Level on May 14th, we used several polls to gain insight on how people are thinking about the post-pandemic world. The topic of the roundtable was “Rehearsing Post-Pandemic Futures.” You can view a video of the virtual roundtable Here. I posted the results of polls One and Two earlier. You can participate in those polls by visiting the posts. The third poll that we launched during the session probed the question of jobs.
Assessing A Post Pandemic Future: A Video
What might a post-pandemic society look like? In a Recent Post, I attempted to address that question by taking a journey backward to a similar time; exactly a century ago. What does a backward journey have to do with a post-pandemic society? The answer lies in a famous quote:
“The further backward you look, the further forward you can see” Winston Churchill
My colleagues (Kevin Mulcahy, Rose Rodriguez, and April Harris) created a video that captures the Blog Content: A journey to the past, and then a look ahead. You can find other videos that focus on a reimagined future on this YouTube Channel.
Coronavirus: Permanent Change? 34 Big Thinkers Explore the Possibilities
While the immediate focus of our global health crisis remains on the present, as we approach the other side, many will focus on a post-pandemic future. Painting pictures of possible futures was already critical in this time of rapid change; the pandemic elevates the urgency. I have been sharing the perspectives of many global thinkers in the interest of providing foresight to those who will need it when the focus shifts. A virtual session focused on a post-pandemic society is being planned, and I will likely participate. In discussing that possibility, I was presented with this Article.
The COVID-19 Economic Impact On China and a Glimpse Of The Future
COVID-19 has had a dramatic impact on China’s economy. Jenna Ross at Visual Capitalist describes how the effects on their economy could foreshadow what the rest of the world can expect. While China turns the corner on the health side of the story, the economic side is telling its story. This Article via the World Economic Forum uses visualization to tell this economic story. Countries in the early stages of the outbreak should take notice. Continue reading
COVID-19 Monday Morning News
The COVID-19 crisis is fast-moving with information bombarding us in real-time. On this Monday morning, as we awake to more isolation and rising numbers, there is much to consider. In this Article, the author focuses on three economic scenarios: Easter: an optimistic scenario (25% likely) where isolation leads to a slow return to normal by late April; Summer: the main scenario (55%) where improvements begin in mid-summer; and Winter: the pessimistic scenario (20%) where impact lasts into the winter. Given the expansion of isolation through April in the U.S., the optimistic scenario is all but eliminated from consideration.
Post COVID-19 Economic Recovery Scenarios
This Analysis by the Conference Board underscores how the trajectory of COVID-19 and the economic response over the next few months are uncertain. They developed three scenarios for the course of the US economy for the remainder of 2020. Focusing on future scenarios was already a critical imperative given the pace of change; the current pandemic just underscores the point. The analysis authors from the Conference Board are: Bart van Ark, Executive Vice President & Chief Economist, and Erik Lundh, Senior Economist. Here is an executive summary from the report:
Rehearsing the Future
 I had the pleasure of participating on a radio show titled Geeks, Geezers, and Googlization. Hosts Ira Wolfe and Keith Campagna did a great job of facilitating our discussion about the future. Check out their Summary of our conversation, and/or listen to our conversation via this rebroadcast.
I had the pleasure of participating on a radio show titled Geeks, Geezers, and Googlization. Hosts Ira Wolfe and Keith Campagna did a great job of facilitating our discussion about the future. Check out their Summary of our conversation, and/or listen to our conversation via this rebroadcast.
The Convergence of Science and Technology
In looking at transformative periods throughout history, it is apparent that Convergence was a critical driver of change. While I am still hopeful of the ultimate convergence across societal, political, environmental, philosophic, economic, and business domains, it is clear that convergence is already occurring in the science and technology domains. This synergistic relationship where advances in one domain fuels rapid advances in the other is the force behind our rapid pace. As we saw in the Poll that looked at the catalysts that drive convergence, it is this rapid pace of innovation that many believe will ultimately drive it. This initial convergence is altering long-held Beliefs and Intuitions – eventually forcing convergence across the other domains.
The Ready Room
I had the recent pleasure of talking with Richard Frederick about a number of topics regarding the future. Richard runs a Podcast called The Ready Room; an idea driven by his concern over the decline of civil discourse and the ideological barricades with which so many have surrounded themselves. In his words: “If only we could come out from behind our political fortresses and talk openly with one another and truly seek to open our minds to change, we could regain a shared civic trust.”
The Ready Room is Richard’s way of reaching out to others to begin this discourse. I was happy to be included in this process. You can listen to our discussion below.
Catalyst Poll Results
Updated results: April 9th, 2019. The response has been great, but I’d like to capture more voices. Please consider taking this very short Poll.
In a recent post on What to Expect in 2019, I launched three focus areas for the coming year. This focus attempts to identify the key drivers of change and the outcomes they enable. The three areas are:
- Convergence is one of the key dynamics I expect/hope to see more of this year. A century ago, convergence across multiple domains ushered in unprecedented advancements in human development. Multiple forces will drive a similar level of convergence in the coming decade.
- The pace of innovation and change is often cited as a key difference between the next revolution and prior ones. This is one of the key catalysts driving change, and I expect it to Accelerate.
- I believe the world will experience a burst of Possibilities enabled by these forces of convergence and acceleration
Globalization 4.0
Within the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the World Economic Forum is focused on Globalization 4.0. We are actually approaching Globalization’s Third Act. In a book titled The Great Convergence, Author Richard Baldwin describes the three constraints that have limited globalization: the cost of moving goods, the cost of moving ideas, and the cost of moving people. The first two acts of globalization occurred when the cost of moving goods and ideas dropped. While globalization raised the standard of living in several developing economies, the third constraint limited the breadth of impact.
In his closing chapter, Mr. Baldwin explores the possibility of a third act. This act is driven by dramatic advancements in areas that address the third constraint. If the cost of moving people were to drop, developing nations like South America, Africa, and others could be the beneficiaries of this third act. That aside, the World Economic Forum is looking at global risks and the need for global solutions. They identified Six Questions that must be addressed to make the next wave of Globalization work for all. They correctly state that facing future challenges requires dialog and input from all. Kudos to them for driving the dialog. The six questions are:
- How do we save the planet without killing economic growth?
- Can you be a patriot and a global citizen?
- What should work look like in the future?
- How do we make sure technology makes life better not worse?
- How do we create a fairer economy?
- How do we get countries working together better?
A very good set of questions. You can see how people responded to them by going Here.
Convergence
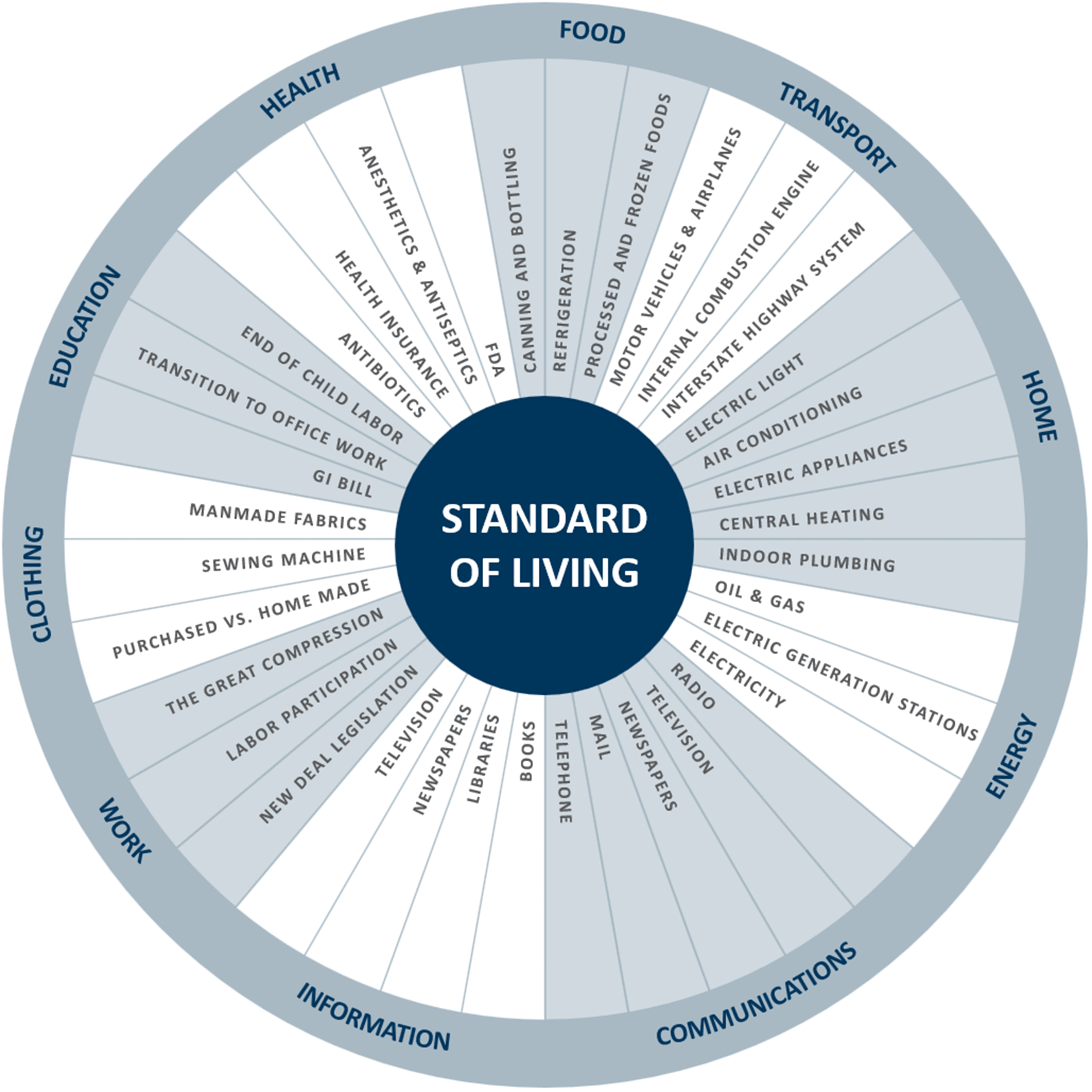
As I described in my Thoughts on 2019 post, convergence is one of the key dynamics I expect/hope to see more of this year. A century ago, a convergence across domains ushered in unprecedented advancements in human development. As Robert J. Gordon describes, the special century (1870 – 1970) that followed the Civil War was made possible by a unique clustering of what Mr. Gordon calls the great inventions. The great inventions of the second industrial revolution significantly improved our well-being. In his view, the economic revolution of 1870-1970 was unique in human history, unrepeatable because many of its achievements could only happen once. What makes this century so special, is that these inventions altered what until then, was a life lived in misery. I captured the advancements made during that period using an Innovation Wheel to map them to our areas of well-being (click on visuals in this post to open in a separate window).
A look at history is very instructive, as several dynamics from that period have the potential to emerge once again – the biggest being the opportunity for convergence. In this context, convergence refers to a virtuous cycle where events in one domain spur action in another. The great inventions (electricity, telephone, and internal combustion engine) were clustered together at the end of the 19th century, forming a virtuous cycle that drove a period of astounding innovation. This innovation cycle continued well into the 20th century – a dynamic that could be emerging again. Yet, science and technology are simply two domains that converged during the special century. The others were the economy, business, politics, and a broader set of societal issues. What enabled this convergence and created the most dramatic improvement in human development? There were several key catalysts.