Fast Future Research provides a glimpse into possible futures through a series of recently published books that focus on our Our Emerging Future and accelerate our learning and dialog. As with his previous books, Rohit Talwar enlists several authors in a new book just launched titled A Very Human future. An abstract for the book reads as follows:
As society enters the fourth industrial revolution, a major question arises—can we harness intense technological bursts of possibility to bring about a better world? A Very Human Future illustrates how the evolution of society, cities, people, businesses, industries, nations, and governments are being unexpectedly entangled by exponential technological disruption. This is not a book about technology but an exploration of how we make it serve humanity’s highest needs and ambitions.
In the past, I have attempted to depict aspects of this emerging future using this visual below. The book touches upon several elements of both curves; and the societal factors affecting them both (Explained Here). As a way of sharing some of the book’s messages, I’ve taken short extracts and aligned them to elements of the visual and the broad categories of our emerging future. These categories are: societal tipping points, the areas of our well-being, the science and technology foundation, future scenarios, societal factors, and a future thinking framework. What follows below provides a small window into the books thinking.
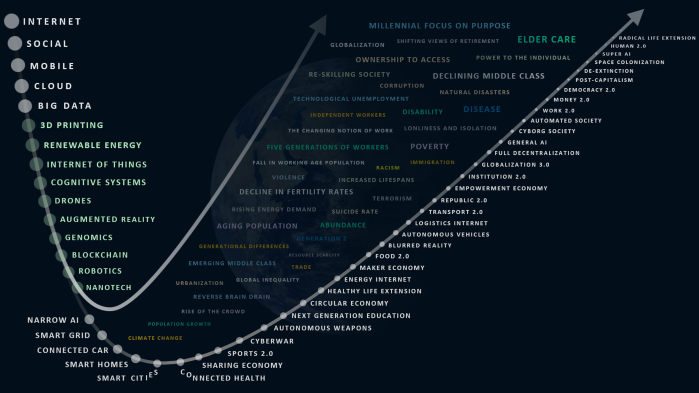
SOCIETAL TIPPING POINTS
As I have positioned via this Blog and through my speaking engagements, I believe society is heading towards its Third Tipping Point. For me, the question is one of degree: how far on a broad spectrum of possible futures will we take humanity? The book explores this question in very imaginative ways:
Fast Future: the augmentation of human beings’ cognitive and intellectual abilities through technological implants, such as memory storage, is a process that is well underway already. Future cyborgs and soft robots could be built out of biological components. For some this is simply the next stage in our evolution and the ultimate way to preserve humanity. A powerful mix of unleashed imaginations applied to disruptive technologies is catalyzing a possibility revolution across every aspect of human life, society, government, and business.
Advances in science and technology will test every assumption we have about how our world works and the purpose of humans within it. The key determinant of whether we survive and thrive in this rapidly changing reality will be our capacity to let go of outdated worldviews, thoughts, beliefs, and assumptions and our ability to learn continuously about the technologies, ideas, and ways of thinking that are shaping the decade ahead.
My Thoughts: true tipping points are driven by fundamental changes in the nature of being human. Several possible futures outlined in the book meet this definition. Our capacity to unlearn is critical in the decades ahead.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOUNDATION
Several elements of the first curve are covered in the book. Below are three elements covered extensively by the authors. They paint a picture of possible futures enabled by each of these elements:
BLOCKCHAIN
Eventually, blockchain ledgers might replace CVs as the best and most immutable representation of one’s professional, educational, and training history. This would prevent people making fraudulent claims and protect against identity theft. For example, as a database of transcripts and credentials, blockchain-based education credits are universal, transparent, and easily verified. Smart devices using a combination of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain would most likely form the basis of a real-life decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). These entities have no human workers or bosses, just a chain of smart contracts triggering—and being triggered by—one another to achieve digitally-enabled tasks across the organization.
BRAIN-COMPUTER INTERFACES
If we get to thought transfer, all sorts of new opportunities emerge. Instant chat really does become instant, emails get replaced by thought exchange, and lies might become a thing of the past. Simply think of a colleague we want to talk to and our AI will be able to determine who it is and connect us as a result of comparing current and historic data on our brainwaves and bodily functions. We might need AI implants in our brain to manage all of this on our behalf and act as a privacy guardian and brain concierge serving up what we need when we need it.
VERTICAL FARMING
it’s estimated that close to 70% of the world’s population will live in cities by 2050, and vertical gardens will help feed hungry urban mouths. We could be able to set up entirely self-sustained farming ecosystems within urban neighborhoods, reducing the environmental impacts of both traditional farming and produce delivery. In this vision, because the majority of larger urban crops will be grown indoors, pests will be nonexistent thus removing the use of pesticides, and disease and contamination could be prevented easily. Farmers will have total control over temperature, humidity, and irrigation, reducing water usage to an estimated 1% of outdoor farming. Controlled lighting will optimize plant growth, thus growing crops at a faster rate than traditional farming. Contained farms additionally offer the option to grow food almost anywhere including in lightless underground structures.
Amazing feats of large-scale city farming have already begun in abandoned factories. Set up inside a repurposed industrial building in Chicago, The Plant is a complete food system which grows vegetables and freshwater fish, brews Kombucha and beer, and produces enough energy from the by-products of these processes to light and heat the entire plant. The world’s largest indoor farm has been built within one of Sony’s old semiconductor factories in Japan. The farm currently ships out 10,000 heads of lettuce a day. PlantLab, a Dutch firm, has developed a contained system in which crops are grown indoors under very specific LED lighting conditions, and the crops use roughly one tenth of the water of a traditional greenhouse. Repurposing old city sites into new city farms holds the promise of providing abundant, fresh, locally grown foods for future urbanites worldwide.
FUTURE SCENARIOS
The second curve on the visual above represents a snapshot of future scenarios that converge to create possible futures. The various dots on the curve will converge in ways that we simply cannot predict. As they do, they provide signals as to where they might lead. Reading those signals and the foresight they deliver fuels our scenario thinking. What follows below is a mapping of extracts from the book to various future scenarios on the curve:
AUTOMATED SOCIETY
Future scenario defined: if the full tipping point referenced earlier is realized, we will live in an Automated Society. There are several levels of automation that range from augmenting humans to human-machine convergence, all the way through to conscious machines. As described, the question is where do we end up on that spectrum?
From Fast Future: roles traditionally thought of as requiring a high-level human intellect are now being automated. For example, AI is now undertaking the work of share analysts and fund managers and doing the bulk of the scanning of medical research and past cases to determine the potential causes of a patient’s symptoms. Similarly, the legal profession is starting to see disruption through AI: automating searches for legal precedents and case reviews, creating and adapting contracts, predicting litigation outcomes, and organizing workloads. What sets AI aside from all other innovations in history is its ability to learn and evolve autonomously. The potential for job loss to precede job creation forces us to consider issues of how we will feed our families, the role of mechanisms such as guaranteed basic incomes, and the potential growth in an underclass completely detached from the rest of humanity.
After collecting massive amounts of data about a person through connected devices, robots (Digital Twins) would be able to replicate this person’s behavior and responses. In fact, your digital twin could attend a meeting for you and comment on your behalf. Your twin could also capture and summarize the entire conversation including analysis of the body language and micro-facial expressions of the other participants and then report back.
HEALTHY LIFE EXTENSION
Future scenario defined: many innovations in science and technology are driving the belief that humans will live longer, healthier lives. Some even believe that this Healthy Life Extension scenario will enable someone already alive today to live to 200 years of age.
From Fast Future: experts believe that organs will be regenerated in vitro and implanted with one hundred percent success rates, similar to plugging new devices into 20th-century computers. Unlimited stem cells could be used to grow or repair any type of organ, in vitro or in situ. Transplant rejection should no longer be an issue, and with the exception of the brain, literally all of our organs should be replaceable by new synthetic, grown or printed ones. Similar to nano-robots, the expectation is that bio-computers will be inoculated into the human body to perform complex tasks, for instance sensing and monitoring the status of organs or repairing tissues and organs in real time.
FOOD 2.0
Future scenario defined: it is said that food hasn’t changed much since it was invented – well all that is about to change. Innovation will lead to new ways of creating food abundance. This second iteration of food comes at a good time, as we live longer, our population grows, and our city centers expand.
From Fast Future: population growth and city expansions are having major consequences, driving a lack of growing space and food in many parts of the world. The growing global population will force us to find creative solutions. Regions with the financial capital may be able to invest in the latest microfiltration technologies, thus allowing constant recycling of waste water into drinkable water. Hopefully, as technology improves, and costs fall, the issues associated with desalination, namely high energy usage and residual salt, could be resolved to such a degree that coastal regions all over the world would be able to afford desalination.
Fruits and vegetables might be grown in buildings controlled by AI rather than on farms, meat could be cloned, and we might see widespread consumption of 3D printed food. Food innovation will see the rise of vertical farming and lab grown meat. Hydroponic plants, fruits, and vegetables might change agriculture as we know it, and help revolutionize the food industry. Having AI-controlled hydroponic vertical farms on the sides of buildings might be one of the solutions. In-vitro cloned meat could be another future solution to our food supply problems. While lab grown meat may still face many challenges, such as flavor control, it also has many advantages such as less waste, less risk of viruses, reduced space requirements, lower emissions, and reduced environmental impacts, among others.
Blockchain is bringing transparency to the food industry with distributed ledgers that verify everywhere a piece of produce has traveled along its journey to the market. Is it possible that eventually it will be someone’s job to track grocery orders on the blockchain, ensuring that food hasn’t been tampered with or traveled through ethically dubious routes?
MONEY 2.0
Future scenario defined: this scenario is not limited to discussions regarding cryptocurrencies. As society shifts from scarcity to abundance, the role of money in society is challenged. What represents value in the future?
From Fast Future: by combining the power of AI and blockchain, the concept of money could evolve into electronic tokens with far more types of assets tradeable within the one “currency.” For example, we might earn tokens from our employment, as rewards from retailers and airlines, and as micro-credits for completing workplace training, school learning tasks, or community service actions. Instead of simply liking a track from a musician, we could now make a micro-payment to them with a fraction of a token. State or community funded tokens could also be given to acknowledge the value of the tasks undertaken by family members performing home care tasks that have traditionally gone unrewarded such as caring for children, the elderly, and the ill. This evolution from cash and cryptocurrencies toward a universal means of exchange could mean the end of cash and foreign exchange markets. Broadening the means of paying for goods and services could allow people to realize the full value of their various dormant assets, such as airline loyalty points, and help address social exclusion.
WORK 2.0
Future scenario defined: there are many current discussions regarding the Future of Work. In my view, the potential for society to rethink the role of work is very high. This is one of several future scenarios that contribute to the tipping point: altering what it means to be human.
From Fast Future: anything that starts to disrupt the relationship between work and individual identity is going to have far-reaching impacts. Some believe that we might be seeing the beginning of the end of jobs as the primary means of feeding our families and that, within 20 years, AI may have transformed the notions of work and employment as we know them. The belief is that these technologies are creating a level of societal abundance that eliminates the need to work and breaks the link between our physical earnings and our access to goods and services. So, as work is gradually and then more rapidly automated away, what becomes of the job? What might a job look like in 2027? Will it still be a “production” role delivering measurable daily outputs, or will a job imply a more creative human activity? Will it still be what people do all day? Conceivably, AI could remove aspects of jobs that tend to be considered “work” while emphasizing the parts of a job that make it a social and enriching activity.
Within five years, it is reasonable to foresee quite significant shifts in the types of jobs available, the skills levels required, and a shortening duration for those roles. On a ten-year timeframe, we could reasonably expect to see widespread automation, a dramatic reduction of the jobs that exist today, new roles emerging in new firms and in existing businesses as they seek to stay competitive, and educationally, a degree or its equivalent could become a minimum entry requirement for 80% or more of all new jobs created. Over the next 15-20 years, organizational structure and the nature of work as we know it seem likely to undergo drastic changes.
NEXT GENERATION EDUCATION
Future scenario defined: our education system must prepare individuals for the world that is, not the one that was. It must ensure that those educated embody the qualities and competencies essential to life in a society very different than our industrial past. Among them are: creativity, critical thinking, innovative thinking, curiosity, social intelligence, a collaborative spirit, adaptability, entrepreneurial spirit, connecting dots, and knowing how to ask the right questions. Our need for life-long learning and unlearning drives us to Reimagine Education and transform through combinatorial innovations that leverage AI, Mobile, Cloud, Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Big Data, and more.
From Fast Future: the future education and learning landscape will be characterized by an increased “blurring of boundaries” between the different levels and directions of education, between schools, higher education, and industry. This evolving education ecosystem should provide greater flexibility in designing educational pathways tailored to individual needs and combining several education modalities into a lifelong and stimulating learning experience. Technology is increasingly supporting new forms of learning, for instance using virtual spaces and enhanced classrooms for experimentation and full immersion in learning settings not achievable otherwise. Over time these will likely include ever-more powerful simulations, intelligent conversational agents, and brain-to-machine or even brain-to-brain interfaces.
Several factors must be considered as we transform the education paradigm: our understanding of how the world is changing; our capacity to think, reason, and solve problems; our ability to learn new skills and approaches quickly; our mastery of life skills such as collaboration, scenario thinking, coping with uncertainty, and handling complexity; and our digital literacy. We can see a scenario where, within five to ten years, 80% of the new jobs created will require a graduate level education or equivalent. Continuing professional development might have to become compulsory or be incentivized through the tax system to encourage individuals to keep acquiring skills to help them move from job to job. In corporate training, VR could help accelerate the learning process by allowing people to run through multiple real-world scenarios for the application of a skill, for example practicing coaching skills with virtual people that possess different attitudes and personalities. Training can also be done in situ, for example providing a VR overlay to guide a remote maintenance engineer through the removal and repair of an aircraft engine part, when the plane is 10,000 miles from its home base.
REPUBLIC 2.0
Future scenario defined: Republic 2.0 speaks to the changes required to the social contract as it relates to the coming tipping point. For example: citizen accounts with benefits outside of jobs, offering paid family and parental leave, providing a universal basic income, changing licensing requirements to ease employment transitions, enacting a solidarity tax on the top 1 percent, lifetime learning accounts, etc. The steps that some believe move us in this direction are: improving legislative representation, reducing geographic inequities, enacting universal voting, abolishing the electoral college, campaign finance reform, and a solidarity tax.
From Fast Future: many shifts are possible in a 25 year timeframe, leading to tensions between two opposing models: 1) a society where only a few decide for all, either as elected representatives, or because new forms of oligarchic power emerge to exert societal manipulation; and 2) a society with neither classes nor hierarchies, characterized by participatory leadership and new forms of “chaordic” organization, where all have the possibility to co-decide on most if not all issues that matter to them.
Funding a new social contract: a less radical option would be tax enforcement; governments start using technologies such as AI to beef up enforcement and collect what they are rightly owed under the law. Globally, governments are struggling to fund their current commitments and many services are overstretched. There is also strong opposition to raising taxes to fund service improvement. However, this might not be required if people and companies simply paid what they are legally supposed to and didn’t use avoidance mechanisms.
EMPOWERMENT ECONOMY
Future scenario defined: we are entering a third stage of business that focuses on Empowerment. In stage one, companies were in the business of providing products and services. In stage two, companies focused on providing convenience – the current customer experience phenomenon. In stage three, the focus shifts to enabling people to provide for themselves.
From Fast Future: in the coming 20-30 years, our increasingly hyperconnected and immersive lives should enable people to be more empowered than ever to share knowledge, become aware of their environment, and take informed and responsible decisions. Such developments will allow us all to become active players in the global scene. New platforms for social networking could allow citizens to self-organize into communities that emerge as new powers able to exert influence and address shared problems in a more structured, responsible, and concurrent manner.
SMART CITY
Future scenario defined: a smart city is an urban area that uses different types of electronic data collection sensors to supply information which is used to manage assets and resources efficiently. This includes data collected from citizens, devices, and assets that is processed and analyzed to monitor and manage traffic and transportation systems, power plants, water supply networks, waste management, law enforcement, information systems, schools, libraries, hospitals, and other community services.
From Fast Future: we are entering an era that will be marked by exponential innovation changing ideas of asset ownership, delivering radical leaps forward in AI, providing increasingly efficient electric propulsion units for vehicles, and enabling the emergence of genuinely smart city infrastructures. These relatively smooth transitions should lead to other changes in cities, including the removal of redundant traffic signals and the remodeling of some street intersections. The clear benefits for humanity here would include cleaner, more livable, safer cities. In the near future, lampposts, parking meters, and other street furniture could be retrofitted into charging stations—possibly powered by solar energy. Smart roads could feature effective ultra-efficient self-monitoring, self-powering, and maybe even self-repairing mechanisms that will characterize the modern smart city. A combination of environmental pressures, technological progress, and a concerned and active citizenry are laying down the challenge for city leaders and planners.
A leading example of a smart city in operation is Singapore, with its constantly evolving “city brain.” This backbone of technologies helps control pollution, monitor traffic, allocate parking, communicate with citizens, and even issue traffic fines. Singapore’s “brain” is also attempting to modify human behavior; for example, one system rewards drivers for using recommended mapped routes, and punishes those who do not. Ultimately, Singapore’s planners hope to discourage driving, and steer commuters toward greater use of public transportation. The city is planning for a physical environment of 100 million “smart objects” including smart traffic lights, lampposts, sensors, and cameras on its roadways, which will be used to monitor and enforce laws.
Rescue Drones – drones are already available that can target individuals in need of emergency assistance, and either airlift them to safety or provide them with vital life-saving equipment. These drones will become ever-more sophisticated and capable, with the ability to undertake more complex search and rescue missions and perform a growing range of medical procedures on the spot.
Autonomous Drones Monitoring and Repairing Infrastructure – constant status monitoring via connected sensors and use of autonomous repair-bots may allow for continuous and pre-emptive upkeep of physical infrastructure. As soon as a sensor detects a pothole or crack in a bridge, the appropriately skilled fleet of autonomous maintenance drones and robots could be dispatched to repair the bridge before further damage can occur.
SMART HOME
Future scenario defined: our homes are another example of an area of our well-being that has not changed much since the second industrial revolution changed how we experienced our homes. But now, we are on the cusp of another home revolution. From the smart and safe living that it enables, to the empowerment that it provides, how we experience our homes will change significantly.
From Fast Future: personal Drone Security—Small drones may fly around a person’s property, constantly monitoring and guarding against security threats like trespassers or burglars. Additionally, they would alert owners of their guests’ arrivals, and be able to confirm the guests’ identities through video and facial recognition software. Could technology enable properties to lease themselves on the open market—charging literally by the minute or hour? Will homes be state-owned, privately owned, or organized on a sharing economy model? Homeowners will find themselves becoming a hub in a city-wide communication network—one of millions communicating to the same central “brain” of the city. How might rental prices be affected by a home’s capacity to generate income from electricity generation?
AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES
Future scenario defined: by now, most people are familiar with the rapid advances in a vehicles ability to drive itself. Although most vehicles will move towards autonomy, the car is the one making all the headlines. A self-driving car is a vehicle that is capable of sensing its environment and moving with little or no human input. Autonomous cars combine a variety of sensors to perceive their surroundings, such as radar, computer vision, Lidar, sonar, GPS, odometry and inertial measurement units.
From Fast Future: as positive experiences with autonomous vehicles accumulate, we should see the first cluster of municipalities and nations such as Norway and Sweden to outlaw human drivers because the risks are too great and errors too high compared to the safety record of autonomous cars. One big excitement factor is autonomous vehicles which could potentially offer a more personalized service. For example, could autonomous vehicles pick travelers up from their homes and be loaded onto trains at the station? When the train reaches the city center terminal, the “train” would break into component vehicle parts and take each traveler to their end destination, thereby providing a “first mile/ last mile” solution. In future smart cities, self-driving vehicles should be enabled by data to orchestrate smooth mobility with almost no stopping required, other than to let passengers on and off.
An autonomous vehicle might automatically fine its driver should they choose to take the wheel while drunk or override the speed limit. The vehicle might also self-insure—sharing the risk across the pool of autonomous cars on the road. These smart cars might also drive themselves to the shop for repairs—carried out by a team of robots and drones.
SPACE COLONIZATION
Future scenario defined: space colonization (also called space settlement, or extraterrestrial colonization) is permanent human habitation off the planet Earth.
From Fast Future: there are an increasing number of people raising concerns over the Earth’s capacity to sustain a growing population and over the potentially irrevocable environmental damage that results from human activity. Some see the establishment of settlements on other planets as a way of reducing the pressures here on Earth and providing alternative habitats for humanity. Some might see these as only accessible by the ultra-wealthy.
Near Earth orbit is increasingly congested by the remnants of old space missions, obsolete satellites, and the results of accidental collisions and losses. At the same time, the space sector is expected to explode -encompassing everything from asteroid mining and space tourism to the establishment of off-world colonies. In response, dependent upon the type of junk being targeted, different fleets of specialized space craft would be controlled, deployed, and coordinated by Space Junk Removal Supervisors based at contractors’ ground stations. The experience in low Earth orbit will drive new policies, agreements, and procedures to prevent a similar issue developing around the Moon and Mars.
FULL DECENTRALIZATION
Future scenario defined: decentralization is one of those structural changes that make what lies ahead so impactful. According to Wikipedia, decentralization is the process of redistributing or dispersing functions, powers, people, or things away from a central location or authority.
From Fast Future: the evolution of AI could see the emergence of a wide range of fully automated Decentralized Autonomous Organizations including banks, travel agents, and insurance companies
ENERGY INTERNET
Future scenario defined: in his book titled The Zero Marginal Cost Society, Jeremy Rifkin describes how Internet technology and renewable energies are merging to create an Energy Internet that changes the way power is generated and distributed in society – a paradigm shift in energy similar to what occurred in computing. He describes an emergent system with synergies between Five Pillars that drive this paradigm shift: Shifting to renewable energy, Transforming buildings into micro–power plants to collect renewable energies on-site, Deploying hydrogen and other storage technologies to store intermittent energies, Using Internet technology to transform the power grid into an energy Internet, Transitioning the transport fleet to electric plug-in and fuel cell vehicles that can buy and sell green electricity on a smart, continental, interactive power grid.
From Fast Future: the use of smart road technology to charge electric cars on the go could increase rapidly if the early pilots demonstrate cost savings for drivers and road maintenance authorities. In parallel, solar pavement panels and kinetic walkways could capture energy, allowing streets to power themselves. Sunlight and pedestrian usage forecasting tools could help determine potential solar and kinetic supply patterns. This would help energy companies manage peaks and troughs in demand through a decentralized smart energy generation and storage infrastructure.
Eventually, with a growing array of such distributed power solutions, a centralized energy distribution grid for homes and businesses may not be necessary. In the next decades, homes could run on their own energy stores, and preserve enough to share, sell, or store for their own later use. The homeowner would no longer depend on a power company to provide electricity, and the home would reach a “net zero” level of ecological impact; giving back more (if not less) than it takes from nature. A personal wearable device provides personal freedom powered by unlimited energy – capturing and transforming the different forms of energy produced by the body such as motion and heat. This is a decentralized future where the body can actually produce all the energy needed to run society. In this future, we have the freedom to choose what to do with her time because in our daily life we are producing wealth with our own personal energy.
SHARING ECONOMY
Future scenario defined: the sharing economy, also known as collaborative consumption or peer-to-peer-based sharing, is a concept that highlights the ability — and perhaps the preference — of individuals to rent or borrow goods rather than buy and own them.
From Fast Future: changing lifestyles, potentially lower real-term incomes, and smart tracking technology are all driving growth of the sharing economy and scenarios where ownership is becoming obsolete, and more possessions are shared and not owned by one individual. This goes along with the shrinking value of owning something and instead purchasing access to it. Shared items could come insured as part of the deal, thus negating any need for buying individual policies.
SOCIETAL FACTORS
Defining this piece of the visual: these two curves in the visual above – extending beyond our ability to see – are driving societal change, and reacting to societal forces. For example, scientific and technological innovation are increasingly driven by techno-philanthropists that are determined to solve some of the world’s greatest challenges. Look at the mission statement of Singularity University: Our mission is to educate, inspire, and empower leaders to apply exponential technologies to address humanity’s grand challenges. In this case, the progression on our curves is driven by the wealth and societal focus of individuals. On the other hand, the curves are changing society, as societal shifts like the move from ownership to access are driven my innovation across the curves.
From Fast Future: evidence suggests that women from the millennial generation across the globe have not married or had children at the same levels as their predecessors. In November 2017, the World Economic Forum (WEF) estimated that, at current rates, it will take 217 years to close the gap on pay and employment opportunities.
Simulations in VR can be used to increase empathy, appreciate other viewpoints or experiences, and even address mental health problems. The manufacturer of a pain reliever demonstrated VR simulations of migraine headaches to the family members of migraine sufferers as a way to help caregivers understand the traumatic pain of such headaches. Similar empathy exercises might help people gain insights on what it is like to be disabled, dyslexic, elderly, or chronically ill.
A FUTURE THINKING FRAMEWORK
As the book effectively describes, understanding possible futures and ensuring that dialog is happening now is critical. I have long been an advocate of a three-legged stool that supports the process of future thinking: See the future, rehearse it, and adapt to its inevitable shifts.
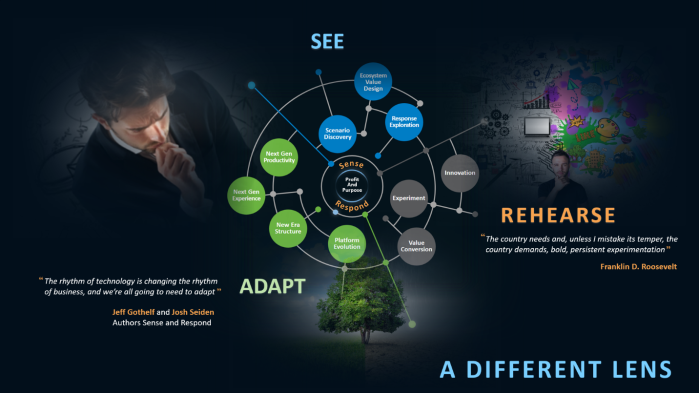
SEE THE FUTURE
From Fast Future: stepping ahead 25 years allows us to break the shackles of current assumptions and constraining beliefs to explore new possibilities and stimulate constructive dialogue. In many cases those scenarios posit a better future for most of humanity. However, there are a number from the use of AI to transhumanism which will polarize views, and in many cases, it is hard to see a coming together on one global perspective. Indeed, there are relatively few issues today where we could claim global support for a particular desired future.
Societal shifts, disruptive thinking, and game-changing technologies are shortening the gap between concept emergence and translation into a physical reality. Hence, the growing emphasis on acting faster on insights and reducing the time to “sell” a change internally—because people can see for themselves why it’s needed. The implication is that everyone needs to learn to understand how to scan and evaluate signals of impending change around them and on the horizon. The only certainties are that: 1) ignoring the emerging future will store up problems; and 2) trying to apply yesterday’s or today’s solutions to the future’s challenges will almost certainly fail.
The use of virtual reality in support of future thinking – in a variety of contexts, people will be able to create different virtual worlds and test alternative strategies, explore possible solutions, and surface unintended consequences. For example, when launching a new product to a new market, the creation and exploration of parallel virtual market entry scenarios would enable employees to evaluate which choice might best fit the current strategy.
REHEARSING
From Fast Future: the freedom and capacity to conduct rapid market-facing experiments is critical—as is the need to have people across the organization seeking out and connecting with emerging businesses and sectors and their respective associations. These market-focused conversations are critical to understanding how current and future sectors and opportunities might evolve. The goal is to gain early access to what might become important future revenue streams. Such a journey requires a highly empathetic, trusting, and nurturing relationship with employees where technology is seen as a means of allowing them the time to be creative, innovative, experimental, and customer-centric.
WELL-BEING
In a brilliant journey through the economic history of the western world, author Robert J. Gordon looks at The Rise and Fall of American Growth. This recent book focuses on a revolutionary century that impacted the American standard of living more than any period before or after. Our standard of living is typically viewed as the ratio of total production of goods and services (real GDP) per member of the population. But this measure fails to truly capture enhancements to our well-being. Human well-being is influenced by advances in the areas of food, clothing, shelter, energy, transport, education, health, work, information, entertainment, and communications. The special century (1870 – 1970) that followed the Civil War was made possible by a unique clustering of what the author calls the great inventions. Clearly – as the visual I developed depicts – the great inventions of the second industrial revolution significantly improved our well-being:

From Fast Future: reimagining clothes – Soon, we will see device recharge technology built into clothing fabrics, conductive fibers woven into fabric that provide processing capacity for wearable devices, and GPS tracking devices fitted into shoes. A Utility Jacket is a totally safe and secure everyday fashion item that keeps mobile devices connected using built-in chargers and a personal private data network. The jacket might also collect, convert, store, and distribute kinetic and heat energy from the wearer’s body and the sun to sell back to the local power grid
There are a great number of other examples in the book that provide a glimpse into these bursts of possibility. I highly recommend the book. Thanks to Rohit Talwar and team for their service in this critical area.

[…] describe the future that is 2019 is with this phrase: Bursts of Possibilities. In the book titled A Very Human Future, the authors focus on an exploration of how we make the above described convergence serve […]
LikeLike
[…] this post will focus on possibilities. As described recently, I believe the world will experience a Burst of Possibilities enabled by the forces of convergence and acceleration. We should expect these possibilities to […]
LikeLike
[…] believe the world will experience a Burst of Possibilities. However, unless we as humans can Unlearn, we are trapped in a way of thinking that undermines our […]
LikeLike
[…] 2019, I described the Three Focus Themes for the year. They were Acceleration, Convergence, and Possibilities. Little did I know that one of those themes would factor so prominently in 2020. In a recent […]
LikeLike
[…] viewed this debate through the lens of an emerging future that is bursting with possibilities. To explore this topic further, I overlaid the potential for future innovation on top of […]
LikeLike