Over the last several years, the big four technologies of the third platform (Social, Mobile, Big Data, and Cloud) have received the lion share of attention, and an emerging class of innovation accelerators like The Internet of Things will capture attention in the coming years. But there are also a number of supporting technologies that serve as enabling components of multiple disruptive scenarios. In some recent presentation preparation work, I focused on technologies like Near Field Communications (NFC) and iBeacon. It was fascinating to find broad applicability across many of the disruptive scenarios on the visual I have used to describe the coming paradigm shift.
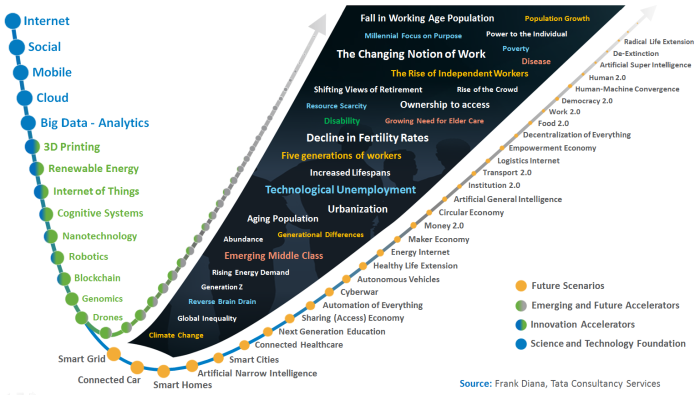
So let’s take a closer look at this impact, with a focus on NFC. Near Field Communications is an ecosystem that intersects multiple industries. It is a wireless technology with very limited range that allows electronic devices to communicate with each other when they’re touched together, or brought within a few centimeters of each other. NFC can be used with a broadening set of devices, including computers, smart phones, appliances, smart televisions, and a growing selection of wearable technology. The tap-and-go technology is becoming a critical tool in creating new, personalized interactive experiences.
Forecasts
ABI predicts that the number of available NFC-enabled handsets will soar five-fold in the next five years to reach 3.5 billion globally by 2019. With a doubling projected this year from 500 million to more than a billion NFC-enabled devices, the time for NFC is now. Mobile payments made via NFC-enabled devices continue to be the most talked about application. In Japan, NFC is used on close to 65 million handsets by 15 million customers initiating 30-50 million transactions per month with 750,000 merchants. There are several key NFC application areas that should explode in the next five years:
NFC becomes an enabling piece of the Internet of Things in a fast, seamless, secure way. A simple tap allows humans to connect with objects to initiate all kinds of interactions. This capability enables entirely new experiences and business applications, while gathering data about each interaction and delivering a valuable source of insight to drive personalization. These new business applications enable emerging ecosystems to deliver value across a number of disruptive scenarios.
The one that everyone is talking about is mobile payment – thanks in part to Apple entering the mix. Mobile payment volume will grow at a five-year compound annual growth rate of 172%, with volume rising to $818 billion by 2019, or just under 15% of total US payment volume according to BI Intelligence. Some key things to consider regarding this NFC application area:
- Platform: mobile phones become the world’s primary financial transaction platform
- Ecosystem: mobile payment success relies on creating an ecosystem of stakeholders – Apple excels here
- Experience: Apple Pay has the most compelling experience and will lead in experience mindshare
- Disruption: mobile payment plays an active role in multiple disruptive scenarios
- NFC: Only 2% of US retailers have the technology in-store
Payment is just the tip of the iceberg, as a deeper look at NFC’s role shows application across a number of emerging ecosystems. Embedded NFC tags for instance can enable a Smartphone to serve as the display for an appliance, simplifying product design and leveraging the common, seamless experience of our Smartphones. Here is a broader look at the role that NFC plays across multiple disruptive scenarios:
Connected Car
- Access: unlock your car, access secure parking garage, restricted parking spaces, fast Internet
- Personalization: adjust your seats, set mirror positions, stream music, temperature
- Payment: Pay for parking, gas, drive-thru meals, car rental
- Information: Warnings of traffic, emergencies, accidents
- Delivery: groceries or parcels delivered directly to car via virtual key
- Entertainment: web-based entertainment, audio, communications
- Data: fuel consumption, mileage and service data
Connected healthcare
- Access: user authentication, patient identification
- Personalization: quantified self, behavior tracking and modification
- Payment: mobile payment for service
- Information: monitor and record vital statistics, store and share personal health information and records
- Health management: medication reminders, chronic condition management, track patient visits, record activities performed by health care workers
- Experience: place medicine refill order when running low, eliminate filling out forms
- Data: exchange data between medical devices
Sharing Economy
- Access: virtual keys provide easy access for multiple people to a single vehicle or house
- Personalization: individualize the shared driving experience by quickly establishing climate, seating, entertainment, information and communication settings
- Experience: have a much more familiar driving experience in an unfamiliar car
- Payment: seamlessly pay for and drive vehicle, pay for other shared products or services
- Notification: messages pushed to indicate car or house accessed
- Management: as sharing extends to everyday objects, NFC enables sharing management
Logistics internet
- Vision: famous Economist Jeremy Rifkin envisions a transformed transportation and Logistics Industry, where a Logistics Internet completely disrupts our centuries old view of warehousing and distribution
- Enablers: the Internet of Things (IoT) is critical to achieving this vision, and sensors, NFC, and WiFi are all enablers of IoT implementations
- Data: technologies like BLE and NFC are in effect sensors that provide more data to aid transportation and logistics processes
- Platform: a platform is required to realize the Logistics Internet vision, and technologies like NFC play a role in delivering against this vision
Energy Internet
- Vision: famous Economist Jeremy Rifkin envisions a transformed Energy Industry, where an Energy Internet enables the delivery of renewable energy at near zero marginal cost
- Enablers: the Internet of Things (IoT) is critical to achieving this vision, and sensors, NFC, and WiFi are all enablers of IoT implementations
- Platform a platform is required to realize the Energy Internet vision, and technologies like NFC play a role in delivering against this vision
Smart City
- Access: transportation, facilities, parking
- Payment: pay parking meter, taxi, parking fees, car sharing service, permits
- Information: smart billboards, events, transit schedules, and delays
- Experience: interact with advertisements and bulletin boards
- Efficiency: smart meters to regulate energy consumption and allow for prepayment using NFC
- Services: first responders access critical medical information
- Public Safety: determine if smartphone user is in the driver’s seat
Smart Home
- Access: unlock doors, temporary access for visitors
- Configure: single tap addition of new smart home devices
- Control: control the smart home from NFC-enabled device, extend displays
- Information: wine-storage cabinets download perfect temperature settings for a particular collection of wines
- Experience: tap frozen dinner to the microwave to use optimal settings, fast product and warranty registration
- Personalization: room temperature, favorite music, etc.
- Maintenance: initiate replacement part purchase, single tap access to repair information, guidance, parts, manuals, etc.
Next Generation Automation
- Actions: passive NFC tags represent a very low-cost approach to enabling actions
- Ecosystems: enabling connected ecosystems like connected cars, smart homes, and smart cities
- Enterprise automation: either as part of their on-board circuitry or as a sticker, NFC tags instruct each piece of equipment on which steps to perform at a given point – Manufacturing
- Field service example:
- Open web-based knowledge base
- Notes on the maintenance carried out
- Log arrival at client premises for SLA reports
- Log the start of a service trip in a field service app
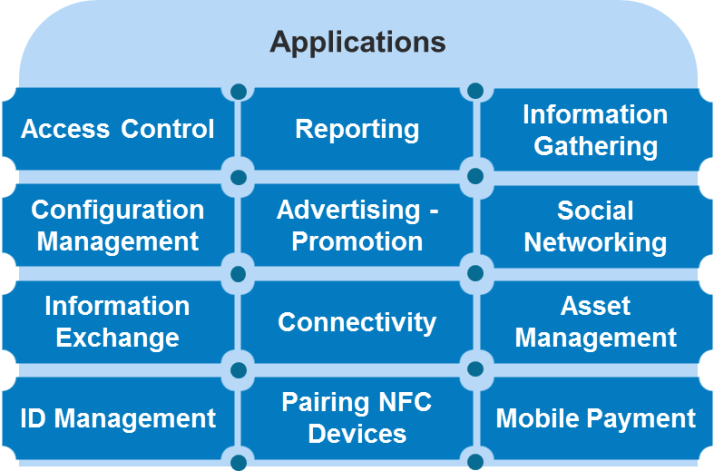
Beyond disruptive scenarios, there are three broad areas of impact to consider: engagement, experience, and next generation of shopping:
Next Generation Shopping
- Access: Store deals, store Wi-Fi, rewards account, multimedia content, real-time store inventory, etc.
- Personalization: relevant coupons, discounts, and reward points
- Payment: build digital shopping cart while shopping, mobile payment upon checkout
- Information: view nutritional and product information, pricing, reviews, etc.
- Experience: personalization and ease of shopping
- Marketing: push offers based on location in store (Beacon)
- Asset Management: NFC phones used for inventory control
Engagement and Experience
- Personalization: connectivity (IoT, NFC, etc.) and Insight (Big Data, Analytics) enable deeper, more personal experiences
- Social: sharing contacts, photos, videos or files and entering multi-player mobile games
- Information: a beacon at a bus stop tells you when the next bus will arrive, the physical world talks about itself
- Payment: mobile payment improves the experience across multiple scenarios
- Interactive: information enabling, and engaging with the physical world creates interactive experiences
- Engagement: connectedness drives engagement
This is a great example of combinatorial innovation at work, or the combining of multiple building blocks in a way that rapidly creates value. So let’s add another set of building blocks to our growing mix:
Those companies that effectively combine these building blocks – to better enable the organization or deliver value to the market – will be winners in the end. Have you considered the role of NFC?


[…] Over the last several years, the big four technologies of the third platform (Social, Mobile, Big Data, and Cloud) have received the lion share of attention, and an emerging class of innovation acc… […]
LikeLike
RF technology is the underlying technology for many IoT scenarios. Many listed as being enabled through NFC are actually based in RAIN RFID. Longer range in combination with RTLS will be very powerful
LikeLiked by 1 person
thanks!
LikeLike